Page Not Found
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
About me
This is a page not in th emain menu
Published:
This post will show up by default. To disable scheduling of future posts, edit config.yml and set future: false.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
Framework for automatic tourist itinerary construction.
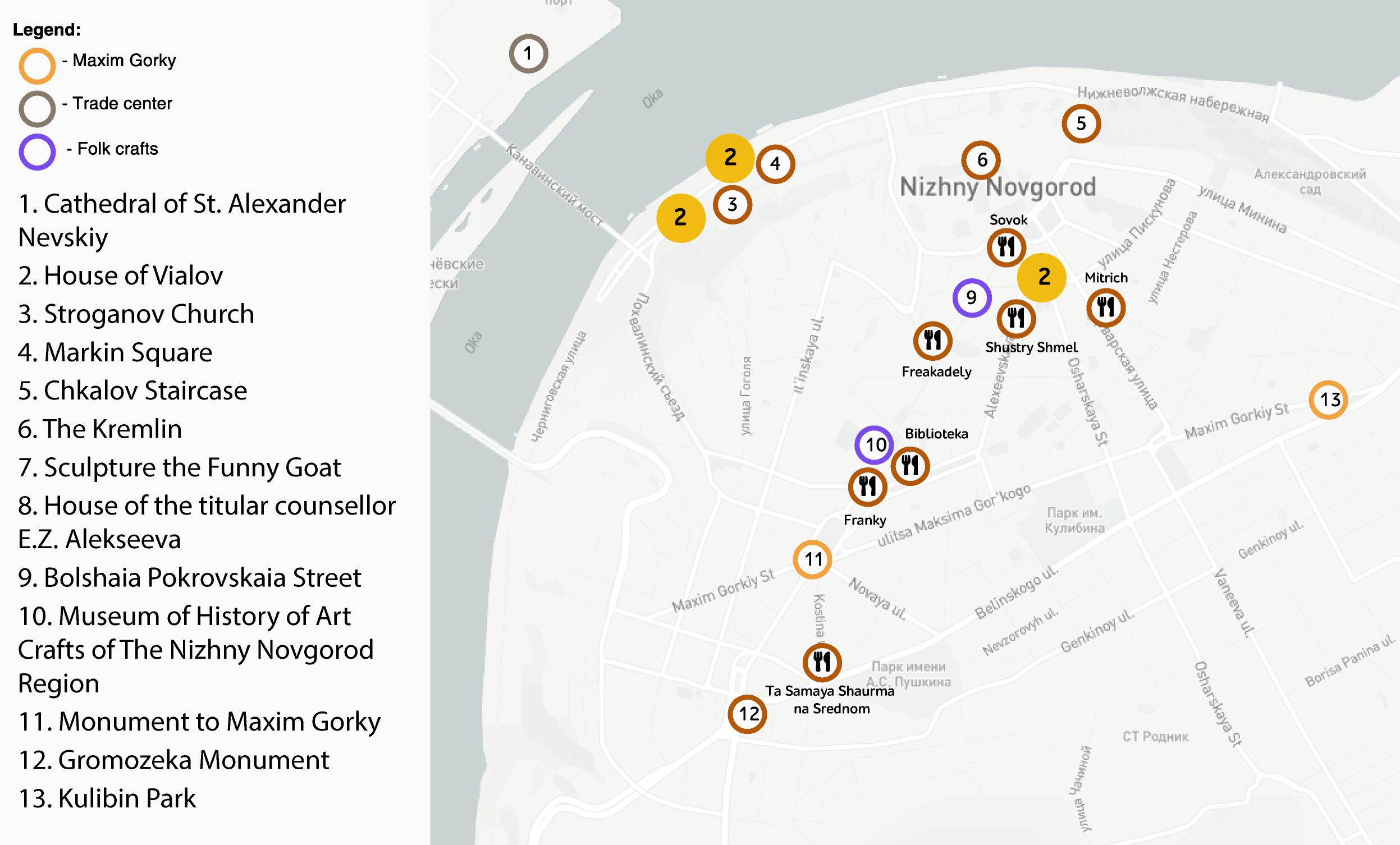
Published:
This paper presents a tool for visualization of the executed processes upon the infrastructure of the cloud computing platform CLAVIRE. Such class of tools is extremely important for the cloud platform developers and the end users, because it gives extensional opportunities for platform processes analyzing by providing interactive mechanisms to supervise over distributed infrastructure networks. The core principles are based on visualization of computational resources' detailed interactions within geographically distributed platform. Our goal was to make a visualization provision tool for more effective understanding, monitoring and managing infrastructure with easy-to-use interface especially for the users who do not have enough technical background to efficiently organize their interoperability with the infrastructure level of the platform CLAVIRE. To manage with this issue, we developed a client-based application that includes a special algorithm based on force-directed graph layout, which is able to represent all aforementioned information on clear and understandable level. © 2015 The Authors.
Recommended citation: Zagarskikh, A., Karsakov, A., Mukhina, K., Nasonov, D. & Bezgodov, A. (2015). An Efficient Approach of Infrastructure Processing Visualization Within Cloud Computing Platform. Procedia Computer Science, 66, 705-710.
Published:
The popularity of travelling by airplanes is constantly growing. Much of existing research describe the global flight market. At the same time, Russian air market is characterized by its peculiarities that have to be identified to build proper models of airfare. The objective of this study is to analyze Russian air transportation market and compare the behavior of prices on local and global flights. Using these data, collected from two independent ticket price information aggregators (AviaSales and Sabre) for the period of spring-summer 2015, an empirical data-driven model was built for air prices prediction for different flight directions. We found that the form of price dependency on purchase earliness differs dramatically between local and international flights in two largest Russian cities (Moscow and Saint-Petersburg). © 2015 The Authors.
Recommended citation: Lantseva, A., Mukhina, K., Nikishova, A., Ivanov, S. & Knyazkov, K. (2015). Data-driven Modeling of Airlines Pricing. Procedia Computer Science, 66, 267-276.
Published:
Data visualization traditionally is the most powerful tool for demonstration and analysis of scientific results and mathematical models in particular. In this paper we introduce the graphical framework for citation graph clustering. Furthermore, we discuss ways to detect factors responsible for scientific groups formation. Two datasets of scientific papers related to different fields were used in this work. Firstly we applied scientometric analysis to our data with the view to determine the most influential keywords. After that, we used two different ways for data clustering-graphic clustering method comprising N-body communication graph and a keyword-based hierarchical clustering. As a result of our studies we propose method for dynamic visualization of scientific papers clusters, built using open-access data. © 2015 IEEE.
Recommended citation: Trofimenko, T., Visheratin, A., Melnik, M., Mukhina, K. & Butakov, N. (2015). Graphical framework for scientific papers clustering. 9th International Conference on Application of Information and Communication Technologies, AICT 2015 - Proceedings, 423-427.
Published:
Video games have become an integral part of the educational process. Born and raised in the digital era, Russian students of the 21st century are seduced by entertainment and in contrast they perceive STEM educational activities as boring and annoying. To spark an interest in Artificial Intelligence (AI) programming we decided to implement a competitive contest in the educational process. By combining the developments of the eScience Research Institute and educational techniques, we have introduced elements of entertainment to a group project of 6 ECTS during the second semester of the Double Degree Master's Program in Computational Science. The main goal of this project is to teach students basics of AI programming by creating bots for a strategy video game. Typical tasks and multi-domain specificity stimulate students to discover and apply new information from available sources promoting the principles of self-education and lifelong learning. An exaggerated and concentrated example of diverse behavioral patterns in the game should help students to transfer the patterns acquired from the games to solve real-life problems.
Recommended citation: Bezgodov, A., Karsakov, A., Mukhina, K., Egorov, D. & Zakharchuk, A. (2015). Learning AI techniques through bot programming for a turn-based strategy game. Proceedings of the European Conference on Games-based Learning, 2015-January, 66-74.
Published:
Modeling of realistic clouds always was one of the most important problems in creating any virtual scenes outside. It has always been an extremely valuable feature for great variety of applications: from flight simulators or meteorological software to computer games especially with an open world. In this work the algorithm of rendering flat clouds in real-time is presented. The hemispherical grid was designed to fill natural placement of clouds. Tools for high-quality visualization of stratocumulus clouds were created. The model of light scattering through clouds is described. This approach allows rendering realistic clouds evolving through time at high frame rates. © 2015 The Authors.
Recommended citation: Mukhina, K. & Bezgodov, A. (2015). The Method for Real-time Cloud Rendering. Procedia Computer Science, 66, 697-704.
Published:
In this paper the sedimentation process of nanoparticles which have distribution in sizes was studied. The mathematical model under consideration gives a rise of velocity which resembles Rayleigh-Taylor instability. The numerical solution is consistent with results predicted by the model. The maximum value of concentration, where instability does not occur, was found.
Recommended citation: Mukhina, K. & Chivilikhin, S. (2015). Theoretical investigation of sedimentation process for nanoparticles statistical ensemble. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 643(1).
Published:
Despite being widely visible on the web, Internet-promoted commercial sex work has so far attracted limited attention from the side of researchers. Current studies outline the issues that new forms of sex work are associated with, however, very little is known to date about their spatial manifestation. In this research we follow the environmental perspective in spatial analysis of crime and deviance with the assumption that the location of venues for provision of commercial sex work can be modeled via the algorithms trained on the distribution of possible correlates in the proximity to the existing venues. Visualization of the acquired results is presented herein along with the errors and score metrics for evaluation of the applicability of specific methods of machine learning. The paper is concluded with the estimation of potential extensions and peculiarities of data used in the research. © The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Recommended citation: Voloshin, D., Derevitskiy, I., Mukhina, K. & Karbovskii, V. (2016). Identifying Venues for female commercial sex work using spatial analysis of geocoded advertisements. Procedia Computer Science, 80, 345-355.
Published:
Mobile phone communication is an important part of human life. Nowadays a great variety of scientific works are dedicated to the investigation of the calls and cellular networks. Efficient analysis of such networks can be a great source of the information useful for reconstruction and simulation of social phenomena. The main goal of this work was to understand how much information can be obtained from the communication network and build an algorithm, which would help to gather information about users' behavior. We used a calls network to reconstruct the underlying contacts network and to detect the strength of relationship between people in this network. Evaluation results show that the developed algorithm can determine users' classes and relationship between users with high quality. © 2016 IEEE.
Recommended citation: Trofimenko, T.B., Mukhina, K.D. & Visheratin, A.A. (2016). Mobile contacts network reconstruction using call domain records data. Proceedings - 2016 3rd European Network Intelligence Conference, ENIC 2016, 55-60.
Published:
This paper presents a concept for visualization of simulation processes in temporal networks. Core principles are based on interactive real-time visualization of complex networks and dynamic processes. Any modifications in simulation parameters result in division of a timeline into branches. Described concept was integrated into an extended tool for visual analysis and tested on a model of interbank interaction. Proposed developments significantly improve process of visual analysis: pattern detection, search of distinctions and etc. © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Recommended citation: Mukhina, K., Guleva, V. & Karsakov, A. (2016). Temporal Branching Approach for Visual Exploration of Simulation Process in Dynamic Networks. Procedia Computer Science, 101, 407-415.
Published:
The influence of non-spherical nanopartides' shape on sedimentation process was studied. Six different shape of particles were considered. From proposed mathematical model it was shown that for non-spherical nanoparticles the perturbation of Z-component of velocity is slightly lower comparing to spherical particles. © Published under licence by IOP Publishing Ltd.
Recommended citation: Mukhina, K.D. & Chivilikhin, S.A. (2016). The influence of non-spherical nanoparticles' shape on sedimentation process. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 741(1).
Published:
Public healthcare can be cast as a complex systems and network analysis is one of the methodological approaches that are commonly used to study these types of systems. In this paper we describe a multi-scale and multi-level interpretation of complex networks in public healthcare. Our contribution is to provide a toolbox for visualization and visual data-driven analysis of complex multiscale temporal contact networks that allows to simulate various dynamic processes using user-defined models. An example of explorative analysis of a dataset from real clinical data obtained from the Federal Almazov North-West Medical Research Centre in Saint Petersburg is described. © The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Recommended citation: Karsakov, A., Moiseev, A., Mukhina, K., Ankudinova, I.N., Ignatieva, M.A., Krotov, E., Karbovskii, V., Kovalchuk, S.V. & Konradi, A.O. (2016). Toolbox for visual explorative analysis of complex temporal multiscale contact networks dynamics in healthcare. Procedia Computer Science, 80, 2107-2118.
Published:
Information spreading simulation is an important problem in scientific community and is widely studied nowadays using different techniques. Efficient users' activity simulation for urgent scenarios is even more important, because fast and accurate reaction in such situations can save human lives. In this paper we present multi-layer agent-based network model for information spreading simulation in urgent scenarios, which allows to investigate agents' behavior in a variety of situations. This model can be used for live city simulation in integration with other agent-based human interaction models. Experimental results demonstrate logical consistency of the proposed approach and show different cases of information spreading in the network with different social aspect. © The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Recommended citation: Visheratin, A.A., Trofimenko, T.B., Mukhina, K.D., Nasonov, D. & Boukhanovsky, A.V. (2016). Urgent information spreading multi-layer model for simulation in mobile networks. Procedia Computer Science, 80, 2086-2097.
Published:
Information spreading analysis is an important problem in the scientific community and is widely studied today using different techniques, from the data analysis to the agent-based modelling. For some extreme situations, like fire or flood, there is little or no reliable information about users’ activity available. That is why an efficient simulation of the urgent scenarios is very important, because analysis of the simulated data can help to provide fast and accurate reaction and save human lives. In this paper, we present a multi-layer agent-based network model for the information diffusion simulation in the urgent scenarios, which allows to investigate agents’ behavior in a variety of situations in the absence of the real data. This model can be used for the urban scenarios simulation in the integration with other agent-based human interaction models. Experimental: results demonstrate good results in comparison with existing works in this area and give a number of insights regarding the further model development. © 2017 Elsevier B.V.
Recommended citation: Visheratin, A.A., Trofimenko, T.B., Mukhina, K.D., Nasonov, D. & Boukhanovsky, A.V. (2017). A multi-layer model for diffusion of urgent information in mobile networks. Journal of Computational Science, 20, 129-142.
Published:
During vacations, people try to explore new places, but it is impossible for tourists to see all interesting locations. In this paper, we shed the light on differences between favorite places of tourists and locals using Instagram profiles. The time windows based identification method is proposed to distinguish visitors from residents. The list of potential tourists' attraction points in Saint Petersburg was obtained by analysis of locals' popular places. © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Recommended citation: Mukhina, K.D., Rakitin, S.V. & Visheratin, A.A. (2017). Detection of tourists attraction points using Instagram profiles. Procedia Computer Science, 108, 2378-2382.
Published:
Given the complexity of modern biological data it is essentially crucial to accord a consistent expounding. Interpreting such data into complex networks and visualizing them can reveal understanding of various processes in a cell. A consequence mapping of signal transduction processes to the spatial genome structure can benefit new insights in interaction detection in the spatial arrangement of genes. We present an approach for multiscale dynamic visualization of signal transduction processes with detailing of target-genes activation in spatial genome structure. The usage of this approach is demonstrated for the WNT signaling pathway in a human cell. We conclude with suggesting future research questions to improve our approach by considering new available data. © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Recommended citation: Bureiko, K., Semashko, M., Mukhina, K.D. & Karsakov, A. (2017). Multiscale dynamic visualization of signal transduction processes with detailing of target-genes activation in three-dimensional genome structure. Procedia Computer Science, 119, 182-189.
Published:
Nowadays, social networks play an important role in many aspects of people's life and in traveling in particular. People share their experience and opinions not only on specialized sites, like TripAdvisor, but also in social networks, e.g. Instagram. Combining information from different sources we can get a manifold dataset, which covers main sights, famous buildings as well as places popular with city residents. In this paper, we propose method for generation of walking tours based on large multi-source dataset. In order to create this dataset, we developed data crawling framework, which is able to collect data from Instagram at high speed. We provide several use cases for the developed itinerary generation method and demonstrate that it can significantly enrich standard touristic paths provided by official site. © 2018 FRUCT Oy.
Recommended citation: Mukhina, K.D., Visheratin, A.A. & Nasonov, D. (2018). Building City-Scale Walking Itineraries Using Large Geospatial Datasets. Conference of Open Innovation Association, FRUCT, 2018-November, 261-267.
Published:
Recent advances in unsupervised salient regions detection algorithms made possible to obtain high-quality saliency predictions without human annotated data. In this paper, we explore the possibilities of semi-supervised salient region predictions using neural networks. We built a fully-convolutional deep architecture and performed controlled experiments training the same architecture from the ground up while using differently generated data as labels. We show that efficient combination of multiple unsupervised saliency prediction algorithms has a consistently positive impact on the predictions generated by a deep model. Despite the increase in model performance, we show that supervised models are still vastly superior in terms of quality. © 2018 The Author(s).
Recommended citation: Mbogo, G.-K., Visheratin, A.A. & Mukhina, K.D. (2018). Deep semi-supervised salient regions detection using joint predictions of unsupervised models. Procedia Computer Science, 136, 183-189.
Published:
Active development of modern cities requires not only efficient monitoring systems but furthermore forecasting systems that can predict future state of the urban area with high accuracy. In this work we present a method for urban area prediction based on geospatial activity of users in social network. One of the most popular social networks, Instagram, was taken as a source for spatial data and two large cities with different peculiarities of online activity-New York City, USA, and Saint Petersburg, Russia - were taken as target cities. We propose three different deep learning architectures that are able to solve a target problem and show that convolutional neural network based on three-dimensional convolution layers provides the best results with accuracy of 99%. © 2018 FRUCT Oy.
Recommended citation: Mukhina, K.D., Visheratin, A., Mbogo, G.-K. & Nasonov, D. (2018). Forecasting of the Urban Area State Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Conference of Open Innovation Association, FRUCT, 2018-November, 268-275.
Published:
Increasing popularity of social networks made them a viable data source for many data mining applications and event detection is no exception. Researchers aim not only to find events that happen in networks but more importantly to identify and locate events occurring in the real world. In this paper, we propose an enhanced version of quadtree - convolutional quadtree (ConvTree) - and demonstrate its advantage compared to the standard quadtree. We also introduce the algorithm for searching events of different scales using geospatial data obtained from social networks. The algorithm is based on statistical analysis of historical data, generation of ConvTrees representing the normal state of the city and anomalies evaluation for events detection. Experimental study conducted on the dataset of 60 million geotagged Instagram posts in the New York City area demonstrates that the proposed approach is able to find a wide range of events from very local (indie band concert or wedding party) to city (baseball game or holiday march) and even country scale (political protest or Christmas) events. This opens up a perspective of building a simple and fast yet powerful system for real-time multiscale events monitoring. © 2018 ACM.
Recommended citation: Visheratin, A.A., Mukhina, K.D., Visheratina, A.K., Nasonov, D. & Boukhanovsky, A.V. (2018). Multiscale event detection using convolutional quadtrees and adaptive geogrids. Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGSPATIAL International Workshop on Analytics for Local Events and News, LENS 2018.
Published:
Data provided by social media becomes an increasingly important analysis material for social scientists, market analysts, and other stakeholders. Diversity of interests leads to the emergence of a variety of crawling techniques and programming solutions. Nevertheless, these solutions have a lack of flexibility to satisfy requirements of different users and individual crawling scenarios, that can range from a simple query to a complex workflow containing multiple steps and requiring data from different networks to be collected. To address this problem, our paper proposes an approach based on a developed domain specific language (DSL) and architecture of distributed crawling system. The DSL has a declarative style that requires the user to define the description of needed data and based on an ontological model of social networks and the essential crawling techniques. Thus, the crawling system can be applied to collect the data from different online social networks within complex workflows along with the exploitation of various crawling methods implemented in a distributed computing environment. © 2018, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Recommended citation: Butakov, N., Petrov, M., Mukhina, K., Nasonov, D. & Kovalchuk, S. (2018). Unified domain-specific language for collecting and processing data of social media. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 51(2), 389-414.
Published:
In this work, we show how social media data can be used for the improvement of touristic experience. We present an algorithm for automated touristic paths construction. Score function for location depends on three components: location’s social media popularity and rating, distances of place from others in route, and location’s relevance to the city unique features. Obtained walking paths were compared to real itineraries prepared by experts for city visitors. Survey results demonstrate that respondents prefer automated routes over existing routes from touristic services. We also created touristic itineraries for 11 cities that host FIFA World Cup 2018. For each city, these routes take into account their specific features related to historical and cultural background. © 2019 Copyright held by the owner/author(s).
Recommended citation: Mukhina, K.D., Visheratin, A.A., Nasonov, D. & Manovich, L. (2019). Intelligent sightseeing in immensely manifold cities: Case of 2018 FIFA World Cup host cities. LocalRec 2019 - Proceedings of the 3rd ACM SIGSPATIAL International Workshop on Location-Based Recommendations, Geosocial Networks and Geoadvertising.
Published:
Orienteering problem (OP) is a routing problem, where the aim is to generate a path through set of nodes, which would maximize total score and would not exceed the budget. In this paper, we present an extension of classic OP—Orienteering Problem with Functional Profits (OPFP), where the score of a specific point depends on its characteristics, position in the route, and other points in the route. For solving OPFP, we developed an open-source framework for solving orienteering problems, which utilizes four core components of OP in its modular architecture. Fully-written in Go programming language our framework can be extended for solving different types of tasks with different algorithms; this was demonstrated by implementation of two popular algorithms for OP solving—Ant Colony Optimization and Recursive Greedy Algorithm. Computational efficiency of the framework was shown through solving four well-known OP types: classic Orienteering Problem (OP), Orienteering Problem with Compulsory Vertices (OPCV), Orienteering Problem with Time Windows (OPTW), and Time Dependent Orienteering Problem (TDOP) along with OPFP. Experiments were conducted on a large multi-source dataset for Saint Petersburg, Russia, containing data from Instagram, TripAdvisor, Foursquare and official touristic website. Our framework is able to construct touristic paths for different OP types within few seconds using dataset with thousands of points of interest. © 2019 Mukhina et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Recommended citation: Mukhina, K.D., Visheratin, A.A. & Nasonov, D. (2019). Orienteering Problem with Functional Profits for multi-source dynamic path construction. PLoS ONE, 14(4).
Published:
Today advanced research is based on complex simulations which require a lot of computational resources that usually are organized in a very complicated way from technical part of the view. It means that a scientist from physics, biology or even sociology should struggle with all technical issues on the way of building distributed multi-scale application supported by a stack of specific technologies on high-performance clusters. As the result, created applications have partly implemented logic and are extremely inefficient in execution. In this paper, we present an approach which takes away the user from the necessity to care about an efficient resolving of imbalance of computations being performed in different processes and on different scales of his application. The efficient balance of internal workload in distributed and multi-scale applications may be achieved by introducing: a special multi-level model; a contract (or domain-specific language) to formulate the application in terms of this model; and a scheduler which operates on top of that model. The multi-level model consists of computing routines, computational resources and executed processes, determines a mapping between them and serves as a mean to evaluate the resulting performance of the whole application and its individual parts. The contract corresponds to unification interface of application integration in the proposed framework while the scheduling algorithm optimizes the execution process taking into consideration the main computational environment aspects. © 2019, Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Recommended citation: Nasonov, D., Butakov, N., Melnik, M., Visheratin, A., Linev, A., Shvets, P., Sobolev, S. & Mukhina, K. (2019). The multi-level adaptive approach for efficient execution of multi-scale distributed applications with dynamic workload. Communications in Computer and Information Science, 965, 675-686.
Published:
In today's world, it is crucial to be proactive and be prepared for events which are not happening yet. Thus, there is no surprise that in the field of social media analysis the research agenda has moved from the development of event detection methods to a brand new area - event prediction models. This research field is extremely important for all sorts of applications, from natural disasters preparation and criminal activity prevention to urban management and development of smart cities. However, even the leading models have an important disadvantage: they are based on prior knowledge about events being expected. So forecasting systems based on such models are heavily limited by a list of events that can be predicted and all events of other types will be out of systems' scope. In this work, we try to address this issue and propose a deep learning model, which is able to predict an area of the future event in the urban environment. This model is able to predict the future state of the city - a level of users activity in the location-based social network Instagram - with the average deviation from the ground truth of 1%, and achieves 69% recall when solving the events prediction problem. © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Recommended citation: Mukhina, K.D., Visheratin, A.A. & Nasonov, D. (2019). Urban events prediction via convolutional neural networks and Instagram data. Procedia Computer Science, 156, 176-184.
Published:
One of the areas that gathers momentum is the investigation of location-based social networks (LBSNs) because the understanding of citizens’ behavior on various scales can help to improve quality of living, enhance urban management, and advance the development of smart cities. But it is widely known that the performance of algorithms for data mining and analysis heavily relies on the quality of input data. The main aim of this paper is helping LBSN researchers to perform a preliminary step of data preprocessing and thus increase the efficiency of their algorithms. To do that we propose a spatiotemporal data processing pipeline that is general enough to fit most of the problems related to working with LBSNs. The proposed pipeline includes four main stages: an identification of suspicious profiles, a background extraction, a spatial context extraction, and a fake transitions detection. Efficiency of the pipeline is demonstrated on three practical applications using different LBSN: touristic itinerary generation using Facebook locations, sentiment analysis of an area with the help of Twitter and VK.com, and multiscale events detection from Instagram posts. © Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2020.
Recommended citation: Mukhina, K., Visheratin, A. & Nasonov, D. (2020). Spatiotemporal filtering pipeline for efficient social networks data processing algorithms. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), 12142 LNCS, 86-99.
Published:
Abstract: In this work, we consider a problem of predicting the next state of a given area using retrospective information. The proposed concept of hierarchical context transfer (HCT) operates on several spatial levels of the input data to overcome major issues of next state prediction problems - density variability, a significant difference between consecutive states and computational complexity. The custom loss function allows assimilating contexts of spatial levels into each other to further improve prediction quality. The proposed deep learning model (HCT-CNN) allows generating precise high-resolution predictions of the target area. We evaluate our model on the use case of predicting the next state of the urban area using a large dataset for six cities - New York, Moscow, London, Tokyo, Saint Petersburg, and Vienna. Experimental results demonstrate that HCT-CNN generates low- and high-resolution predictions of better quality than existing methods.
Undergraduate course, ITMO University, High-Performance Computing Department, 2017
Introductory course to GIS, 2016/2017 spring.